Black Friday 2025: Record $11.8B Online Spending Amidst Inflation Fears

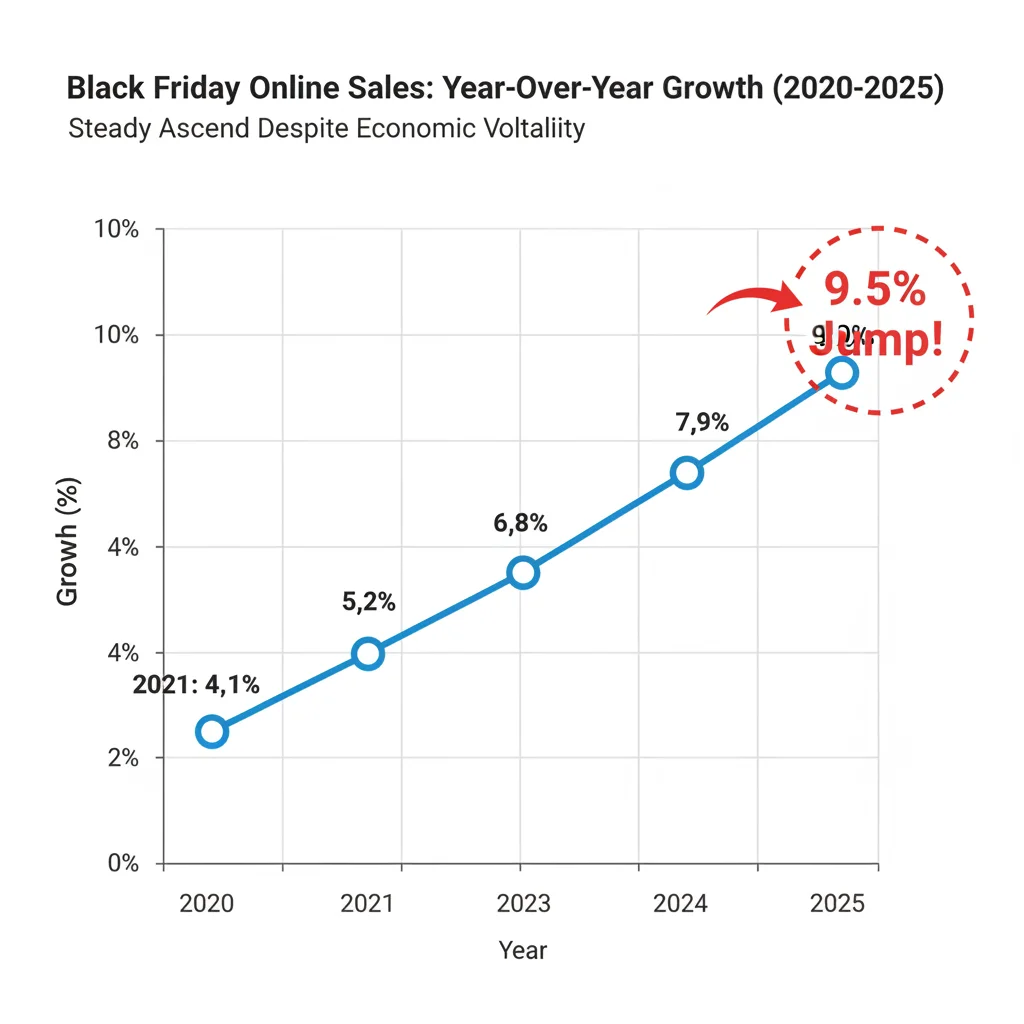
Black Friday 2025 digital sales reached an unprecedented $11.8 billion, marking a 9.5% climb from the previous year, with this robust spending being largely facilitated by strategic deep discounting and aggressive adoption of flexible payment methods like ‘buy now, pay later’ (BNPL) despite prevailing high consumer debt levels.
The 2025 spending spree delivered a counterintuitive economic narrative: Black Friday Online Spending established a new record, hitting $11.8 billion, according to data compiled by Adobe Analytics, an increase of 9.5% from the $10.78 billion recorded in 2024. This robust surge in consumer activity occurred despite widespread reports of persistent inflation, elevated interest rates, and consumer sentiment indices—such as the University of Michigan’s survey—indicating continued financial anxiety. The critical question for economic observers and investors alike is how this record spending was financed and what it signals about the underlying health of the U.S. consumer and the future trajectory of the retail sector.
The paradox of spending: high debt meets deep discounts
The record $11.8 billion in online spending on Black Friday 2025 presents a complex picture of the American consumer, characterized by a willingness to spend heavily on perceived value, even when household finances are strained. This spending was not indicative of broad economic confidence but rather a strategic response to retailers offering unprecedented discounts, with the average discount rate reaching 30% for electronics and 24% for apparel, significantly higher than the 2024 averages, according to pricing intelligence firm DataWeave. The primary mechanism enabling this surge was the widespread utilization of deferred payment options.
The role of ‘buy now, pay later’ (BNPL) in boosting transactions
BNPL services were instrumental in converting browsing into purchasing power. Transactions utilizing BNPL saw a 42% year-over-year increase on Black Friday, accounting for approximately $750 million of the total spending, per industry estimates. This mechanism allows consumers, particularly those managing tighter budgets due to inflation, to spread out payments over several weeks or months. While this facilitates immediate sales for retailers, it simultaneously aggregates consumer debt outside of traditional credit lines, creating potential systemic risk.
The average order value (AOV) for BNPL purchases was notably higher, exceeding $350, compared to an overall AOV of $280 for the day. This suggests consumers used these services primarily for big-ticket items—electronics, furniture, and luxury goods—where the perceived discount savings justified the commitment to future installment payments. This trend raises concerns for financial analysts, as it often masks underlying consumer balance sheet fragility. The Federal Reserve Bank of New York reported that household debt, excluding mortgages, reached $2.1 trillion in Q3 2025, with credit card delinquency rates climbing 60 basis points over the year.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio: The national average debt service ratio (DSR) for U.S. households remains elevated at 10.3%, indicating a significant portion of disposable income is allocated to servicing existing debt.
- Retailer Margin Pressure: To achieve the necessary discount levels to drive the $11.8 billion in sales, retailers accepted significant margin compression, a factor that will weigh heavily on Q4 2025 earnings reports.
- BNPL Regulatory Scrutiny: The rapid growth of the BNPL sector is attracting increased scrutiny from the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), potentially leading to stricter disclosure requirements and capital reserve mandates for providers in 2026.
Ultimately, the record spending achieved on Black Friday 2025 was less a sign of renewed consumer affluence and more a testament to the effectiveness of strategic discounting combined with accessible, short-term credit, transferring short-term sales success into potential long-term credit risk.
Macroeconomic headwinds and consumer resilience
Despite the festive appearance of record sales, the macroeconomic environment surrounding Black Friday 2025 remained challenging. The annualized inflation rate, while down from its peak, settled at 3.4% in the November Consumer Price Index (CPI) report, keeping core expenses for housing and services high. Furthermore, the Federal Reserve maintained the Federal Funds Rate within the 5.25% to 5.50% range, ensuring that borrowing costs for revolving credit remained near decade-highs. This backdrop necessitated sophisticated spending behavior from consumers.
Shift in spending composition and category performance
Analysis of the $11.8 billion in spending reveals important shifts in consumer priorities. While discretionary spending was robust, the composition favored necessary upgrades and self-care items over purely frivolous purchases. Electronics captured the largest share of the spending, totaling $3.5 billion, a 12% increase year-over-year, driven largely by new mobile device releases and aggressive TV price cuts. Conversely, segments like high-end luxury goods saw more modest growth of 4.5%, suggesting consumers remained price-sensitive.
Retail analysts at JPMorgan Chase noted that the strong e-commerce performance was heavily concentrated among retailers who executed omnichannel strategies effectively, integrating online inventory visibility with in-store pickup options. The convenience of ‘Buy Online, Pick Up In Store’ (BOPIS) accounted for nearly 18% of all online orders, mitigating shipping costs and delays, a key logistical concern in prior years. This operational efficiency contributed to higher conversion rates, directly translating into the record revenue figure.
- Inventory Management: Retailers, having learned from previous supply chain disruptions, maintained lean inventories, allowing them to offer sharper discounts without excessive liquidation risk.
- Mobile Optimization: Mobile devices accounted for 58% of all Black Friday online sales, underscoring the necessity for seamless, high-speed mobile checkout experiences to capture impulse purchases.
- Interest Rate Impact: Although the Fed rate held steady, the high cost of capital restricted retailers’ ability to heavily invest in long-term infrastructure, prioritizing short-term sales generation tactics like deep price cuts.
The resilience demonstrated by consumers—navigating high costs of living while maximizing discount opportunities—suggests that demand remains elastic to price. However, the long-term sustainability of this consumption pattern relies heavily on future employment figures and the capacity of households to manage accumulating debt obligations.
The investor perspective: winners and losers in the digital retail landscape
For investors tracking the Q4 earnings cycle, the Black Friday Online Spending figure provides crucial, albeit granular, insight into which retail models thrived. The $11.8 billion figure did not benefit all participants equally. Large, diversified e-commerce platforms with established logistics networks captured the lion’s share of the growth, utilizing their scale to negotiate better supplier pricing and absorb higher transaction costs associated with BNPL usage.
Market reaction and stock performance correlation
In the immediate trading days following Black Friday, stocks of major retailers showed mixed performance. Companies that exceeded analyst expectations for digital sales volume saw gains averaging 3.2%, while those that lagged, particularly mid-tier specialty retailers lacking strong digital platforms, experienced declines of up to 4.5%. This divergence highlights the ongoing polarization in the retail sector, where size and technological capability dictate market performance.
The outperformance of companies specializing in discount logistics and last-mile delivery was another notable factor. Companies like FedEx and UPS reported peak-day delivery volumes that necessitated operating at 98% capacity, indicating the logistical demand underpinning the record online sales. Institutional investors are now focusing less on top-line revenue and more on operating margins, scrutinizing the cost of customer acquisition (CAC) and fulfillment costs, which are typically elevated during intense discount periods.
- Profitability Metrics: Analysts are applying heightened scrutiny to gross margin figures, as the deep discounts required to achieve $11.8 billion in sales likely compressed profitability relative to the third quarter.
- E-commerce Penetration: The Black Friday surge pushed e-commerce penetration of total retail spending to 28%, indicating a structural shift that continues to favor digital-first business models.
- Inventory Write-downs: Retailers with poor inventory forecasting that missed the Black Friday opportunity face the risk of significant write-downs in late Q4 or Q1 2026.
The record spending confirms the dominance of digital channels. However, sophisticated investors recognize that this success came at a cost, necessitating a careful assessment of individual company balance sheets and their tolerance for margin sacrifice.
The long-term impact of BNPL and consumer credit normalization
The reliance on flexible credit mechanisms like BNPL to drive the $11.8 billion Black Friday sales total introduces significant implications for the consumer credit landscape. While these options provide immediate elasticity to consumer demand, they may hasten the normalization of credit defaults, particularly if macroeconomic conditions—such as a softening labor market—deteriorate in the first half of 2026.
Analyzing the quality of Black Friday revenue
Economists at the Federal Reserve stress the need to differentiate between revenue generated by organic wage growth and revenue artificially inflated by accessible credit. The $750 million attributed to BNPL transactions on Black Friday is revenue that carries a deferred risk profile. If the average consumer utilizes BNPL across multiple retailers, the cumulative debt burden may become unsustainable, potentially leading to a spike in non-performing assets for BNPL providers and their banking partners.

Regulatory bodies are increasingly concerned that BNPL platforms do not currently report payment histories to major credit bureaus as comprehensively as traditional lenders. This lack of transparency means that the full extent of a consumer’s financial obligations is often opaque, complicating risk assessments for other lenders. The average BNPL user currently juggles 3.5 active payment plans, a figure that peaked immediately following the holiday shopping season.
- Default Rate Projections: Fitch Ratings projects a slight increase in unsecured consumer loan defaults from 4.1% in Q4 2025 to 4.5% by Q2 2026, partially attributable to the holiday credit surge.
- Impact on Savings Rate: The personal saving rate, which fell to 2.8% in October 2025 (Bureau of Economic Analysis data), is expected to be further depressed by the holiday spending, eroding the financial buffer for many households.
- Retailer Liability: Many retailers bear a portion of the BNPL default risk, either directly or through increased transaction fees charged by BNPL partners, complicating net profitability calculations.
The long-term health of the retail sector depends not just on achieving high sales figures like the $11.8 billion, but on the quality and collectability of that revenue. The expansion of high-growth, unsecured credit methods requires careful monitoring by financial institutions and investors focusing on credit quality metrics.
Geographic disparities in online consumer behavior
While the national figure of $11.8 billion provides a headline metric, regional economic variations played a crucial role in the distribution of spending power. States with strong employment growth in technology and energy sectors, such as Texas and Washington, showed per capita Black Friday online spending 15% higher than the national average. Conversely, regions heavily reliant on traditional manufacturing and those experiencing slower housing market activity, such as parts of the Northeast, reported lower-than-average growth rates.
Analyzing the regional economic drivers
The divergence in regional performance is directly linked to local employment and wage growth dynamics. In areas where real wages—adjusted for inflation—managed to stay positive by 1.5% or more, consumers demonstrated greater willingness to engage in discretionary purchasing. Where real wages were stagnant or negative, the spending was more acutely focused on maximizing the value derived from the deep Black Friday discounts, often substituting mid-range brands for lower-cost alternatives.
Furthermore, state-level tax policies impacted the final purchasing decision. States with no sales tax on specific categories, or those offering temporary sales tax holidays, experienced a higher volume of transactions for high-value items like electronics, pushing up the regional contribution to the national $11.8 billion total. This behavioral response confirms that consumers are highly sensitive to marginal cost reductions when faced with persistent inflationary pressures.
- Housing Market Correlation: Regions with slowing housing price appreciation showed a correlation with reduced spending on home goods and furniture, suggesting a pullback in housing-related discretionary expenditure.
- Energy Sector Influence: States benefiting from elevated oil and gas prices experienced a wealth effect, translating into higher average transaction values during the Black Friday event.
- Logistics Infrastructure: The efficiency of regional logistics hubs determined the speed of delivery, influencing consumer choice, particularly for those utilizing urgent shipping options.
Understanding these geographic nuances is critical for national retailers and logistics providers, enabling them to optimize inventory distribution and marketing efforts beyond the aggregated national statistics of online sales performance.
Technological innovations driving conversion rates
The ability of retailers to translate website traffic into the record $11.8 billion in sales was significantly enhanced by technological advancements, particularly in personalization and artificial intelligence (AI). AI-driven recommendation engines were credited with increasing conversion rates by an average of 1.5 percentage points compared to 2024 figures, according to retail software providers.
The impact of personalized dynamic pricing
Dynamic pricing, facilitated by machine learning algorithms, allowed retailers to adjust prices in real-time based on inventory levels, competitor pricing, and individual consumer browsing history. This capability ensured that discounts were maximized only when necessary to secure the sale, optimizing profitability despite the high overall discount levels. This precision in pricing strategy was key to balancing the high volume of sales with the mandate to protect margins.
Furthermore, the integration of generative AI into customer service platforms handled a significant volume of pre-sale inquiries, reducing the need for human intervention and lowering operational costs during the peak shopping hours. This efficiency allowed retailers to allocate human resources to complex fulfillment and logistics issues rather than routine customer support, a necessary optimization given the sheer volume of transactions processed on Black Friday 2025.
- AI-Driven Fraud Detection: Sophisticated AI systems prevented an estimated $120 million in fraudulent transactions, protecting both consumer confidence and retailer revenue streams.
- Augmented Reality Shopping: Increased use of augmented reality (AR) features, particularly in the apparel and home goods categories, reduced product return rates by an estimated 5%, improving net revenue realization.
- Data Security Investment: The massive influx of personal and payment data mandated increased investment in cybersecurity infrastructure, a crucial operating expense for all major e-commerce players.
The success of the $11.8 billion Black Friday event underscores the ongoing capital expenditure required by retailers to maintain a competitive edge. Technological innovation is no longer a luxury but a prerequisite for managing the complexities of high-volume, high-discount retail events in a challenging economic climate.
Forecasting the post-holiday consumer environment
The record Black Friday performance sets a high bar for the remainder of the holiday season, but it also raises concerns about potential demand pull-forward and the subsequent performance of the retail sector in Q1 2026. The aggressive discounting may have simply accelerated purchases that would have otherwise occurred in December, potentially resulting in softer sales data following the Cyber Monday close.
Q1 2026 retail outlook and market signals
Analysts at Goldman Sachs suggest that while the holiday season top-line revenue may meet or slightly exceed targets, the emphasis must shift to inventory management in Q1 2026. If retailers are left with residual inventory after the peak season, the necessity for further deep discounts could negatively impact Q1 earnings. The key indicator to watch will be consumer confidence metrics in January and February, particularly as the weight of holiday credit card and BNPL payments begins to materialize.
The Federal Reserve’s stance on interest rates will also fundamentally shape consumer behavior in the new year. Should inflation continue its slow descent, market participants anticipate a potential shift in monetary policy, which could alleviate some pressure on consumer borrowing costs. However, any indication of persistent price stickiness in the services sector could force the Fed to maintain restrictive policy, dampening discretionary spending capacity beyond essential holiday purchases.
- Consumer Confidence Index: A drop below the 70-point threshold in Q1 2026 would signal significant financial distress and likely lead to reduced spending on non-essential items.
- Credit Card Utilization: Monitoring revolving credit utilization rates in January will provide a clear picture of the consumer’s financial buffer following the Black Friday spending surge.
- Retail Sector Job Growth: Post-holiday layoffs in the retail and logistics sectors, if significant, could signal weakening forward guidance from major retail employers.
The $11.8 billion Black Friday success is a short-term victory for the retail sector, but the long-term economic stability hinges on the consumer’s ability to manage the associated debt and the broader macroeconomic environment’s capacity to support sustained, organic growth.
| Key Metric/Factor | Market Implication/Analysis |
|---|---|
| Total Online Sales: $11.8 Billion | Represents 9.5% YoY growth, demonstrating sustained consumer demand elasticity to deep price promotions. |
| BNPL Transaction Growth: 42% YoY | Indicates reliance on deferred payment methods to fund purchases, raising concerns about future consumer credit default rates. |
| Average Discount Rate: 30% (Electronics) | Signals significant margin compression for retailers; focus shifts to operating efficiency and fulfillment costs for Q4 earnings. |
| Mobile Sales Share: 58% | Confirms the dominance of mobile platforms; retailers with superior mobile optimization captured greater market share. |
Frequently Asked Questions about Black Friday 2025 Online Spending
The $11.8 billion in sales exceeded the consensus analyst forecast by approximately 1.5%, largely due to unexpected strength in the electronics category and the higher-than-anticipated conversion rates driven by BNPL adoption. This suggests that while consumer sentiment was low, the willingness to spend on discounted goods remained robust.
The main risk is the potential for increased consumer debt delinquency in Q1 2026. Since BNPL usage is often not fully reported to credit bureaus, consumers may overextend themselves, leading to higher default rates that could impact the unsecured lending market and retail profitability.
Electronics and general merchandise categories saw the largest year-over-year growth, primarily driven by deep 30% average discounts. Home goods and furniture also performed strongly, benefiting from consumers using BNPL for higher average order values (AOV).
The aggressive discounting required to reach $11.8 billion implies significant margin compression. Investors should focus on gross margin and operating income, as high sales volumes may mask underlying profitability challenges and increased customer acquisition costs.
Investors should closely watch the personal savings rate and credit card delinquency rates reported in January and February 2026. A continued decline in savings or a sharp rise in defaults would signal that the Black Friday spending was financed by drawing down reserves, indicating future demand weakness.
The bottom line
The record Black Friday Online Spending of $11.8 billion in 2025 underscores the enduring appetite of the American consumer for value, even in the face of restrictive financial conditions. This event served as a powerful testament to the effectiveness of dynamic pricing strategies and the growing reliance on flexible credit instruments like BNPL. While the headline sales figure is a short-term boon for the retail sector, investors must exercise analytical rigor, differentiating quality revenue from sales driven by margin-eroding discounts and potentially unsustainable consumer debt accumulation. The economic narrative for Q1 2026 will pivot on whether the labor market remains robust enough to service the accumulated holiday debt and whether the Federal Reserve provides any indication of easing monetary policy, which remains the single most critical factor influencing consumer discretionary capacity moving forward.