
Tariffs, Costs, and Housing: A $10,900 Price Tag on New Homes
Since 2020, US residential construction costs have surged 34% due primarily to rising material prices and supply chain volatility, with tariffs on essential imports like lumber and steel contributing an estimated $10,900 to the final sale price of a typical single-family home, exacerbating housing affordability issues nationwide.

House Prices Rose 2.2%: States Still Offering Value for Buyers
The US housing market saw a 2.2% year-over-year price increase, signaling persistent demand; however, regional disparities mean that states in the Midwest and parts of the South continue to offer strategic value for both first-time buyers and seasoned investors.
Remote Work Still Reshaping Housing: Tech Migration Trends
The enduring shift towards remote work is fundamentally altering US housing dynamics, driving significant capital and demand from traditional coastal tech hubs to Sun Belt and Mountain West metros, accelerating localized inflation and reshaping investment strategies.

Property Taxes Rose 10.4%: How to Challenge Assessments
Property taxes across the United States have increased by an average of 10.4% since 2021, forcing homeowners to confront rapidly escalating valuations; understanding the appeal process is crucial for mitigating this significant financial burden.

Inflation at 3%: Impact on Home Purchase Budgets and Mortgage Strategy
The persistent 3% inflation rate is not merely a headline; it is a structural headwind significantly eroding the purchasing power allocated for housing, mandating strategic shifts in mortgage planning and budget allocation for prospective homeowners in the US.

10% Down Payment: Housing Market Shift Mirrors 1989 Levels
The resurgence of the 10% down payment as a standard in U.S. housing finance, a level not commonly seen since 1989, signals a recalibration of risk and accessibility, particularly benefiting creditworthy first-time buyers navigating high interest rates and elevated home prices.

Fed December Rate Cut: Mortgage Rate Impact Analysis for US Homeowners
The projected Federal Reserve December rate cut is anticipated to lower short-term funding costs, potentially influencing the benchmark 10-year Treasury yield and subsequently easing 30-year fixed mortgage rates, offering relief to prospective US homebuyers.

HELOC Rates at 7.81%: Should You Tap Home Equity Before Rates Rise?
As the average Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) rate hovers near 7.81%, driven by sustained high Federal Reserve policy rates, homeowners must urgently evaluate tapping equity for renovations or debt consolidation, balancing current costs against the probability of future rate hikes.

Energy Efficient Home Upgrades: Claim $3,200 Tax Credit Before 2025
The expanded Energy Efficient Home Improvement Tax Credit, authorized by the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), provides homeowners with a substantial financial incentive, offering up to $3,200 annually for qualifying energy upgrades, significantly reducing the effective cost of capital improvements before the 2025 deadline.
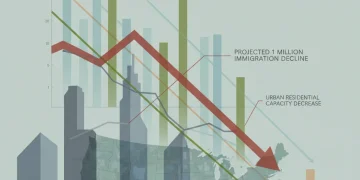
Immigration Decline 1 Million in 2025: Housing Market Impact
The projected 1 million reduction in US immigration for 2025 is set to significantly decelerate housing demand growth, potentially easing rental price pressures in key gateway cities like New York and Los Angeles, according to economic models.